Blockchain is most widely associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, Cardano, etc, and is sometimes erroneously used to refer to cryptocurrencies. One must understand that blockchain is far more than a cryptocurrency. Even though the terms are often mistakenly used interchangeably, they aren’t the same thing.
Most cryptocurrencies are built on blockchain technology. In other words, it is the technology that underpins the cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Bitcoin is the first application of blockchain technology and now the technology is being used for many other applications.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that can be used to store data in numerous locations without the need for a central monitoring system. This lets individuals and businesses store and securely transfer data and currencies in real-time. Without any middlemen or brokers, information is transferred peer-to-peer on the blockchain.
To understand it better, consider how our current systems work. For communications over the internet, we depend on high-performance computers called servers owned by companies. All our communications go through these servers.
The same is the case with money transfers. We depend on banks that will verify and validate our transactions. These servers, institutions, and companies act as intermediaries in our Let us see how in the following sections.
Why the name Blockchain?
As we know that Blockchain is a ledger and transactions are recorded in ledgers. By keeping transactions digitally, blockchains operate as a ledger.
These transactions are organized into “blocks” in this ledger. More blocks are formed when more transactions are added. Each of these blocks is connected to the next. As a result, the term “blockchain” was coined.
In simple words, these blocks are cryptographically confirmed and joined together to form the blockchain, an immutable chain of blocks.
Characteristics of A Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is not maintained on a single server/master computer or controlled by a single firm, bank, or organization. Rather, it is shared among a large number of servers connected to a network.
Permanent and secure
A blockchain’s data is cryptographically secure and distributed to all network participants. This combination of features delivers a high level of security and makes it virtually impossible to disrupt the blockchain.
Blockchain is immutable
In a blockchain, every action is recorded, and nothing is left out. The action is time-stamped and cryptographically secured when it is recorded and stored in a block. Decentralization and cryptography work together to ensure that no single party can alter the blockchain.
What makes up a Blockchain?
Blockchain is made up of three basic parts that are as follows :
- The transaction: Any type of data can be stored on the blockchain in this approach.
- The block: A collection of various transactions.
- The chain: All of the blocks are interconnected.
How does a Blockchain works?
Blockchain is a decentralised ledger that allows thousands of connected parties (computers known as nodes) to keep a record of its transactions. The desired transaction is broadcasted via the peer-to-peer network when a user creates a transaction on a Blockchain network.
The transaction is subsequently confirmed by the network’s nodes. After a transaction has been confirmed, it is combined with other verified transactions to form a new block. After that, cryptographic principles are used to secure the block.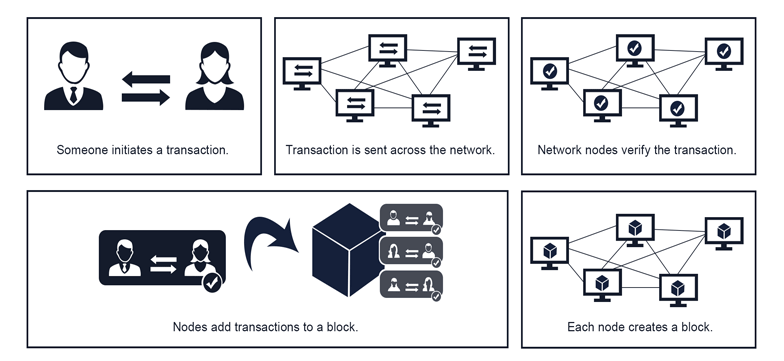
A block will be created by each node in the network. The network chooses one block from this set based on some parameters. The existing Blockchain network is then updated with this block, confirming that it is secure and immutable.
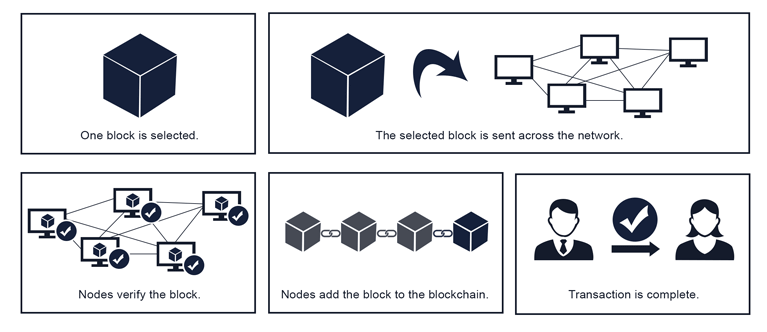
Each blockchain transaction follows the procedures below
- The blockchain network is notified of the transactions. A blockchain network is made up of a collection of machines that run the blockchain software and are connected over the internet.
- The transaction is tested to ensure that it is genuine. The systems in the network analyze the transaction and verify that it is legitimate. This is a decentralised process that takes place among the network’s multiple servers.
- Each transaction is added to a block after it has been confirmed and acknowledged as legitimate. The Blockchain network’s computers authenticate a transaction and add it to a block of other confirmed transactions. There will be multiple transactions in each block. A new block will now be created for every node in the network.
- From the network, one block is identified. A single block from the network is chosen at a certain point in the blockchain in order to maintain network consistency.
- The selected block is then added to the chain. This block is accepted by all computers in the network, and it is added to the blockchain.
Types of Blockchain
Based on the level of decentralization and access, blockchains can be classified as follows:
Public Blockchain: Anyone is welcome to join and take part in the action. What’s going on is visible to everyone. Eg: Bitcoin, Ethereum.
Private Blockchain: The action is governed by a single entity. Only used when the network’s participants are familiar with one another.
Consortium Blockchain: This blockchain combines the benefits of both public and private blockchains. It’s possible that it won’t be open to the public. The network will include multiple partners. The network will be password-protected.
Each of these blockchains, has its unique set of applications and use cases.
So, this is all about blockchain. I hope you find it interesting reading and gaining knowledge about it.